HMIs in Extreme Conditions
Automation systems' employment in hazardous or dangerous activities and locations has evolved to be the standard approach for effectively managing risky or possibly hazardous functions. This is one of the realities of automation systems. Reducing the amount of time workers and technicians are exposed to dangerous environments dramatically lowers the likelihood of safety issues and lessens loss. Remote monitoring of risky activities may be done with a variety of benefits.
Manufacturing automation systems now rely heavily on human-machine interaction (HMI). The potential to employ HMIs in operations where hazardous and dangerous conditions occur that might endanger operators, technicians, or engineers is only one of the numerous uses for them. To maintain the secure and efficient functioning of industrial processes, it is essential to comprehend and use critical methods in hazardous and risky environments. There are many chances to use HMIs in hazardous processes, and when risk mitigation is required, some benefits become obvious.
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) strategies for hazardous areas should prioritize the safety of operators and equipment in such environments. Here are some key strategies that can be implemented:
- Hazardous Area Classification: The first step is to classify the hazardous areas based on the type of hazard present. This will help determine the appropriate HMI equipment and design requirements.
- Robust and Reliable Hardware: The HMI hardware used in hazardous areas must be rugged and reliable, able to withstand extreme temperatures, humidity, and other environmental factors. It should also be designed to prevent ignition and explosion hazards.
- Safety Standards Compliance: The HMI system must comply with relevant safety standards such as IECEx, ATEX, and NEC to ensure that it is safe to use in hazardous areas.
- Proper Training: The operators must receive adequate training on the use of the HMI system and the hazards present in the area.
- Clear and Visible Displays: The HMI displays should be clear and visible, with large fonts and symbols, and color coding where necessary, to ensure that operators can quickly and easily identify critical information.
- Alarm Management: The HMI system should have an effective alarm management system to alert operators to potential hazards in the area.
- Remote Monitoring: Remote monitoring of the HMI system from a safe location can be helpful in hazardous areas. This allows operators to monitor the system without having to be physically present in the hazardous area.
- Maintenance and Testing: Regular maintenance and testing of the HMI system are essential to ensure that it continues to function safely and effectively in hazardous areas.
Overall, the primary objective of HMI strategies in hazardous areas is to ensure that operators can monitor and control processes safely and efficiently while minimizing risks to people, equipment, and the environment. Automation Distribution offers extreme condition HMIs from Exor. Explore some of Exor's Extreme Conditions HMIs below. 
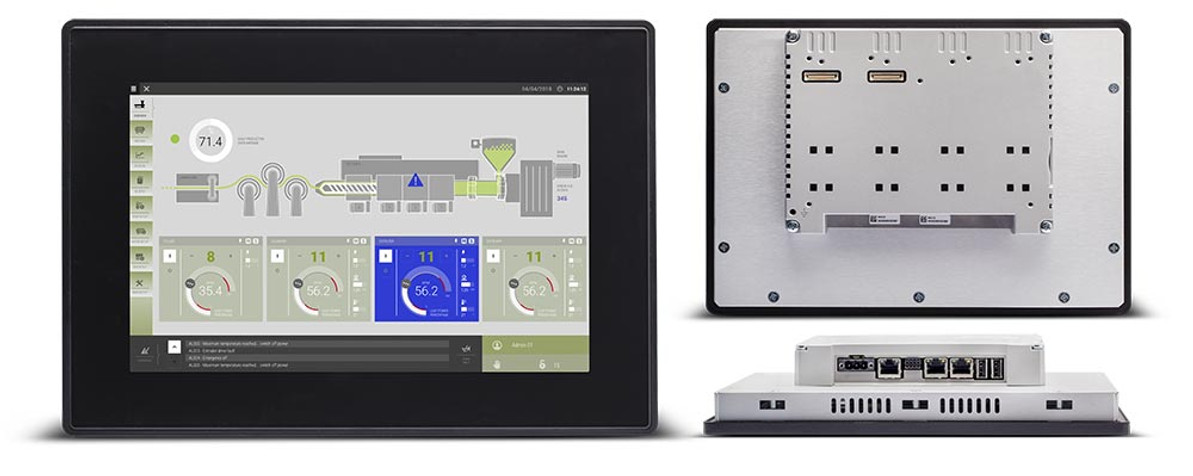
Exor eX710G Extreme Conditions HMI
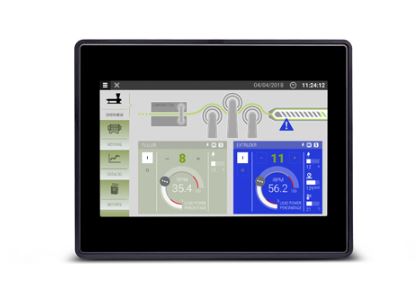
Exor eX707G Extreme Conditions HMI
Sources: ChatGPT, https://www.controldesign.com/displays/hmi/article...
Recent Posts
-
Using Scan Tunnels to Track, Sort and Route Warehouse Packages
If you’re using conveyor lines to move products, packages and shipments through your warehouse, the …Apr 17th 2024 -
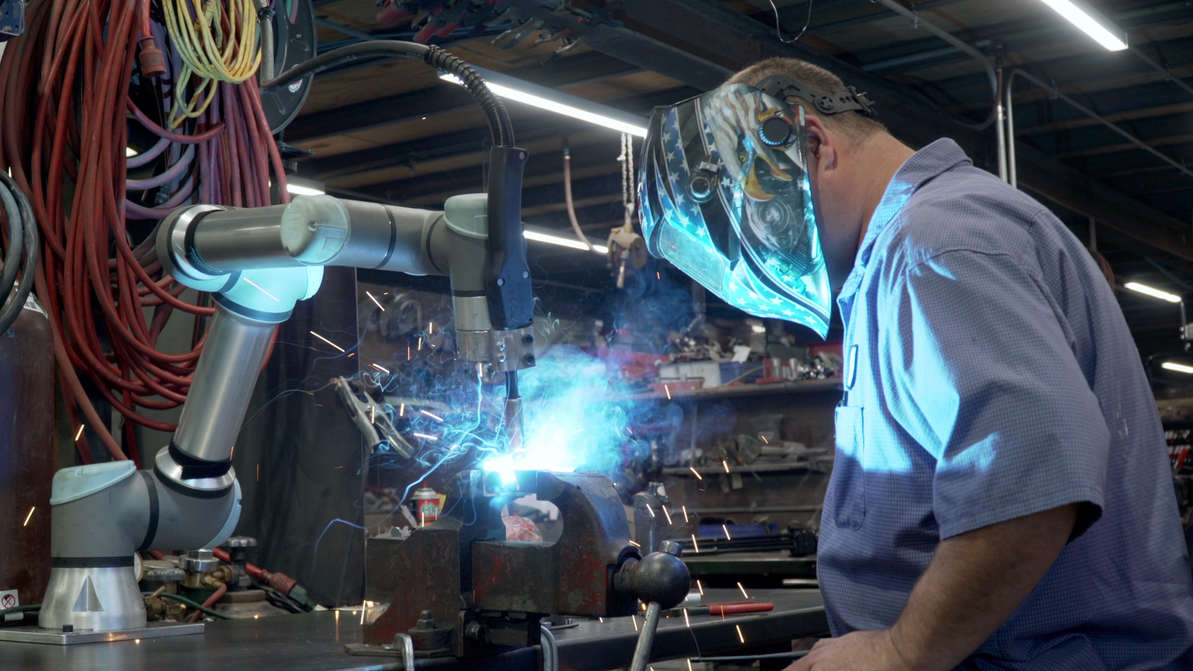
Embracing Collaboration: How Universal Robots Transformed DeAngelo Marine Exhaust
When the welding robots made their debut at DeAngelo Marine Exhaust, there was a mix of excitem …Apr 11th 2024 -
How to Speed Up Your Warehouse Packing by 33% with Machine Vision
Packing benches are some of the busiest areas of most warehouses, with thousands of items to pack i …Apr 4th 2024




